Learning Objectives
After this training, providers will be able to:
- Explain the steps of correctly performing an ECG
- Understand the logistics of obtaining an ECG
- Analyze the ECG tracing to identify missing leads, lead reversal, and common signal artifacts
- Troubleshoot common problems related to ECG acquisition
- Independently obtain a high quality ECG
- Teach learners how to perform a high quality ECG
ECG walkthrough for patients at Cincinnati Children’s
- Order ECG in Epic
- Obtain ECG machine from storage location on A6C, sign log at HUC desk
- Place electrodes (stickers) and connect leads (wires) – detailed instructions below
- For infants you may need to cut electrode stickers in half to fit them across the torso
- Press power button to turn on ECG machine
- Load patient’s ECG order:
- Press F1 “Patient Data”
- Verify 2 patient identifiers (name, DOB, MRN, etc.)
- Option 1:
- Scan patient barcode
- Select the appropriate order (if multiple orders listed)
- Option 2 (if scanner is not working):
- Press F6 “More” > F2 “Main Menu” > F6 “More” > F4 “Order Manager Interface” > F2 “Load Orders”
- Input correct patient location, then press Enter
- Highlight desired patient using Up/Down arrows, press Enter to select patient
- Press F6 “Load Orders” > Order will load to the cart, and patient will be listed in Order Manager > Press F1 “Select” to highlight the patient > Press Enter > Press F2 “Continue” > Patient information will appear on the screen
- Enter your Network ID into the “Performing Tech” field
- Troubleshooting:
- Check back of cart to make sure cords are connected
- Check for green light on back of cart to verify internet connection
- Evaluate electronic ECG tracing. Troubleshoot problems.
- When satisfied with electronic tracing, press “ECG” button to capture
- If unhappy with captured tracing, press F2 “Cancel” to discard and try again
- When satisfied with captured tracing, press F1 “Continue” to print and electronically transmit ECG
- Disconnect leads, remove and discard electrodes
- Clean equipment
- Return ECG machine to A6C, sign log at HUC desk
Proper Lead Placement
Always double check electrode placements and lead connections
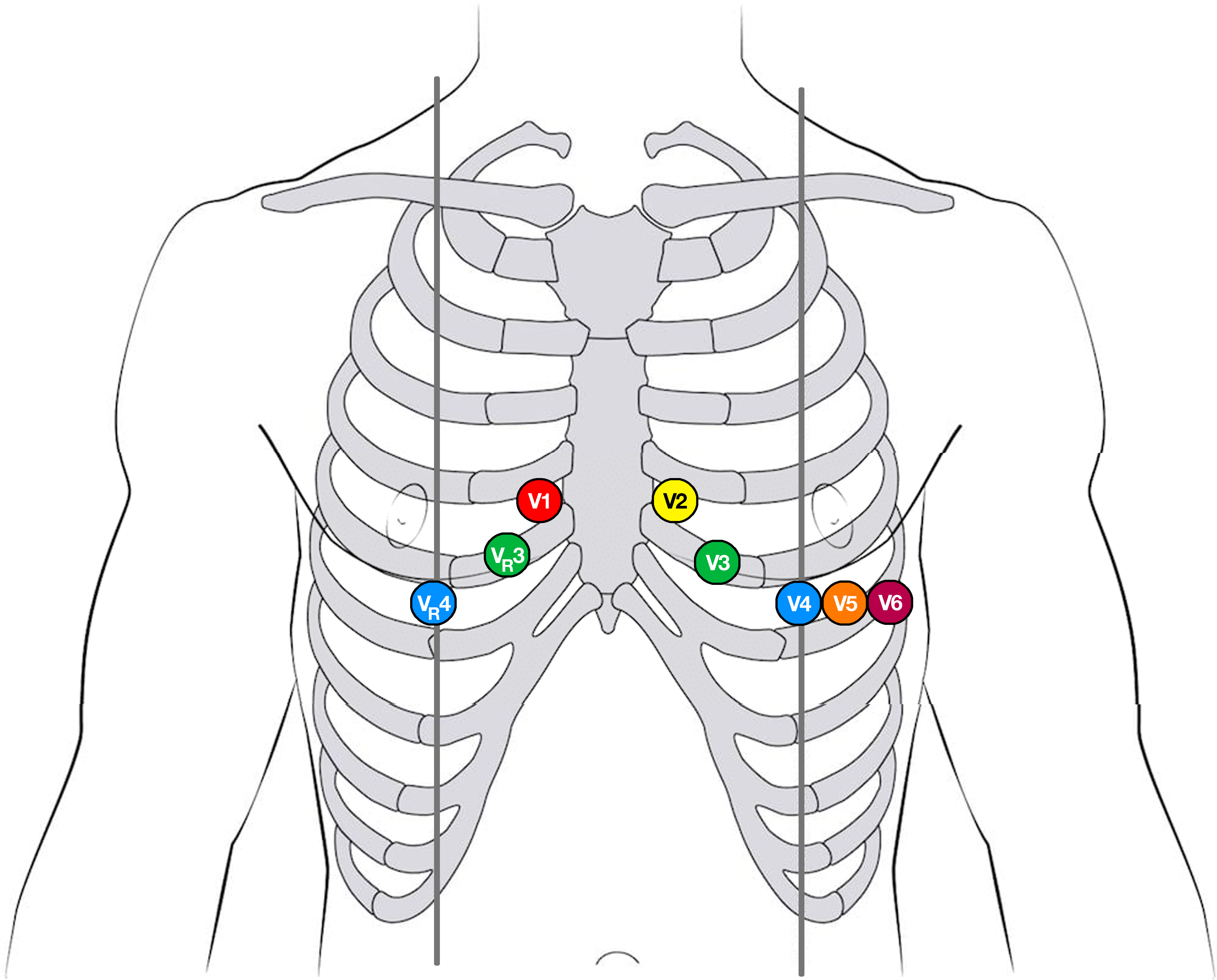
Precordial leads
- V1 – 4th intercostal space, right sternal border
- V2 – 4th intercostal space, left sternal border
- V3 – Midway between V2 and V4
- V4 – 5th intercostal space, left midclavicular line
- V5 – Same horizontal line as V4, anterior axillary line
- V6 – Same horizontal line as V4 and V5, midaxillary line
- V3R – Midway between V1 and V4R
- V4R – 5th intercostal space, R midclavicular line
Limb leads
Limb leads can be placed anywhere on the appropriate extremity, as long as they do not break the torso plane
- RA – Upper right arm
- LA – Upper left arm
- LL – Upper left leg
- RL – Upper right leg (ground electrode)
Troubleshooting
Limb lead reversal
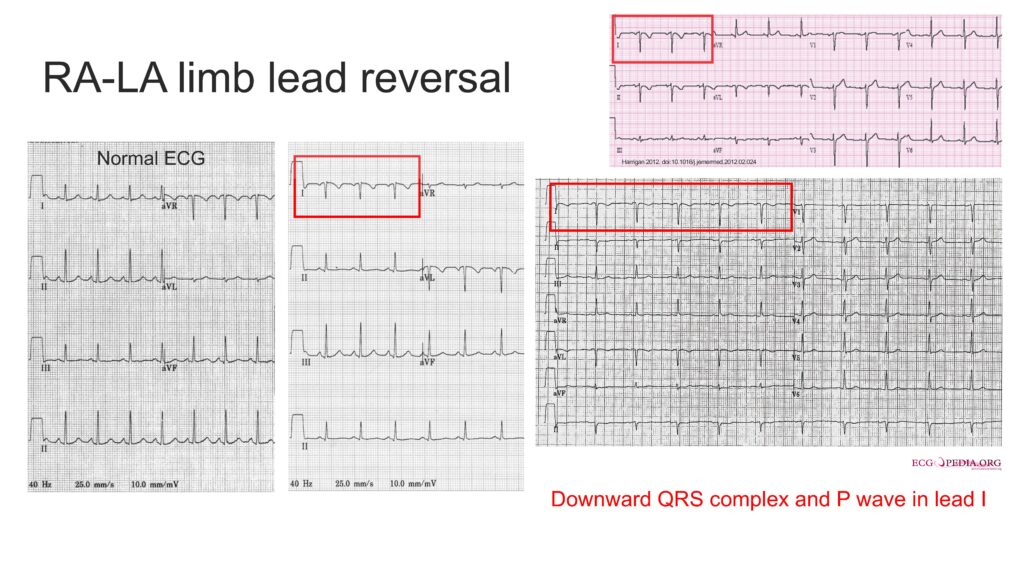
- RA-LA reversal > downward QRS in I
- RA-RL reversal > Isoelectric (flat) signal in II, upright QRS in aVR, downward QRS in I
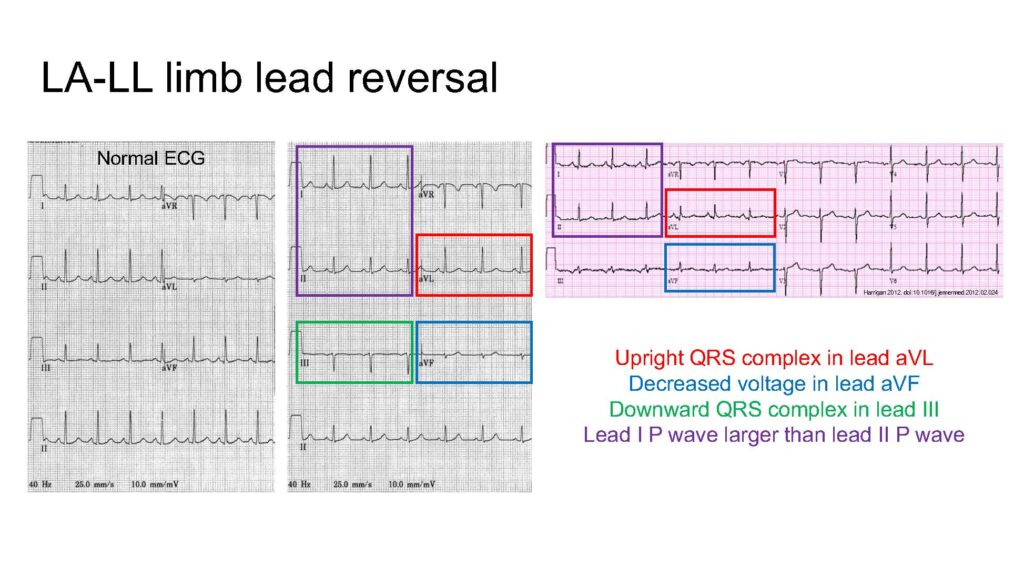
- LA-LL reversal > Upright QRS in aVL, decreased voltage in aVF, downward QRS in III, larger P wave in I compared to II
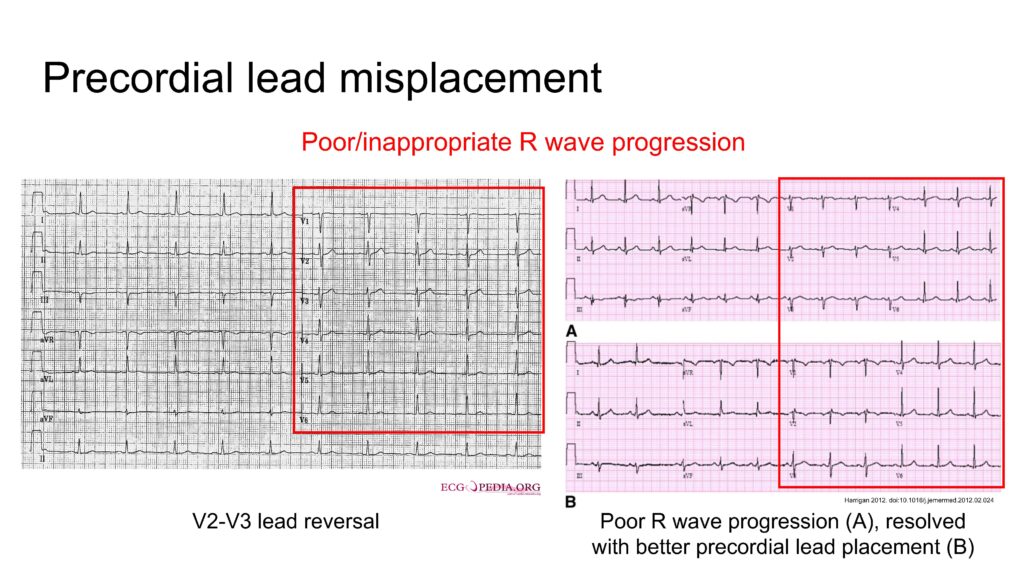
Precordial lead misplacement/reversal
- Poor/inappropriate R wave progression in precordial leads
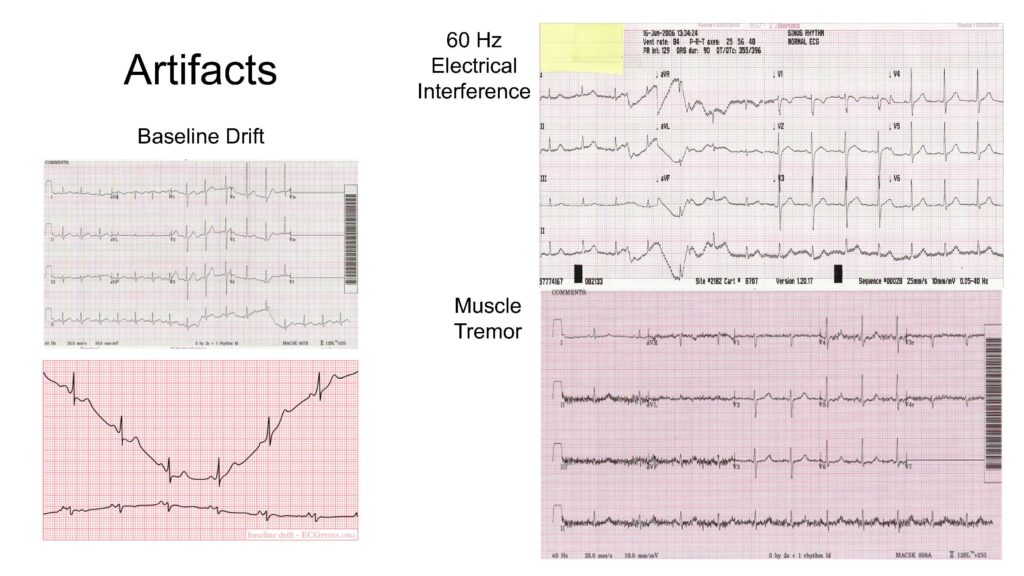
Artifacts
- Patient movement leading to baseline drift
- Muscle tremor leading to noisy signal
- 60-Hz electrical interference leading to oscillating noise in signal
Incorrect scale settings
- Standard voltage (y-axis) is 10 mm/mV
- Higher setting will amplify signal
- Lower setting will dampen signal
- Standard speed (x-axis) is 25 mm/sec
- Higher setting will widen waveforms
- Lower setting will compress waveforms
Electrode and lead issues that reduce ECG quality
- Dry electrodes due to package being left open
- Adhesive buildup on lead wires
- Cracked or damaged lead wires

